Automation of production processes is impossible without the use of specialized information systems (hereinafter IS). Modern IS for production automation are characterized by the use of interconnected databases, knowledge bases, and tools that define the properties and capabilities of a unified enterprise information system. The functioning of such IS is ensured by a corresponding set of software and technical means, with various options for their use. The most common options are:
- Equipment (computing equipment — hereinafter VT) and software (hereinafter PO) are located directly in the company's (enterprise's) offices;
- The use of cloud infrastructure, where computations are performed remotely (cloud computing) on the provider's servers, where the corresponding PO is installed.
In the second case, a model of providing network access on demand to a configurable computing resource is used, which usually has the following properties (defined by NIST-USA):
- On-demand self-service: the consumer can independently determine and change parameters such as access speed, processing time, amount of stored data, etc., without interacting with the service provider;
- Broad network access: the service is accessible from various devices/platforms;
- Resource pooling: the provider's computing resources can be used by multiple consumers;
- Elasticity: resources are allocated and released automatically;
- Measured service: the provider automatically measures the amount of services provided to consumers.
The functionality of services using cloud computing is determined by the following primary service models:
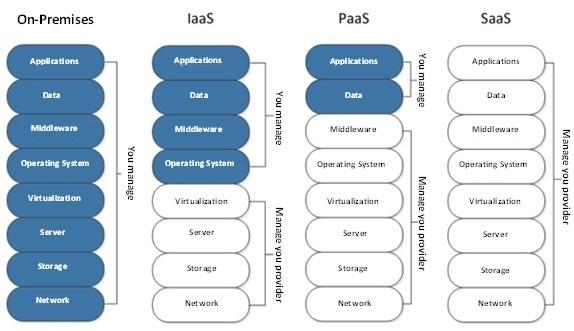
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service);
- PaaS (Platform as a Service);
- SaaS (Software as a Service).
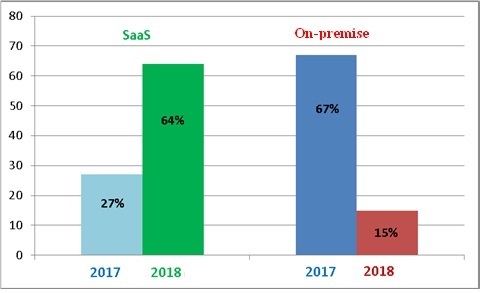
From the user's perspective, the SaaS model based on cloud technologies is the simplest, as the user uses application software without the need for its technical support — the client receives only the application interface and the result. By implementing the SaaS model, the customer significantly reduces initial costs for acquiring software and subsequent license renewals, as well as avoids costs for maintaining software and VT. The SaaS model allows company employees to access computational resources via standard mechanisms for various platforms, ensuring mobile accessibility and eliminating the need to stay attached to a workstation or computer. The SaaS model provides access to the most advanced data processing technologies for a wide range of enterprises. Additionally, SaaS offers advantages such as convenient subscription payment and extensive customization options. These key features have contributed to the popularity of the SaaS model worldwide. According to Panorama Consulting Solutions, the number of respondents who chose the SaaS model in 2018 increased by 37% compared to 2017 and now accounts for 64% of all IS deployment options. The number of respondents choosing local IS decreased significantly from 67% in 2017 to 15% in 2018.
Over the next 2-3 years (according to Pagely), 88% of enterprises plan to invest in SaaS technologies. More and more companies are conducting business operations via smartphones. Besides the aforementioned advantages, it should be noted that the security level of using software in the SaaS model is higher than local hosting.
These security advantages arise because information security solutions for the SaaS model provide more current protection compared to on-premise systems due to several factors:
- Developers and users of the system receive more data on attacks and threats due to the large volume of information for analysis;
- Information on attacks and threats is updated in real-time within the central core of the SaaS product, ensuring regular and timely updates;
- Companies quickly receive advanced technologies, especially when using cloud services for information security or SecaaS (Security as a Service).
In this case, the cost of ownership of such technologies for enterprises is significantly lower compared to similar solutions designed for local systems. Currently, solutions based on Odoo ERP and 1C: ERP WE are proposed for production management and planning. Software modules for integration with SaaS can be installed in these systems, which can also operate in the cloud.
The tasks of operational production planning (management) are of crucial interest to enterprises worldwide. This level of planning involves using complex optimization algorithms to calculate production schedules with minimal latency. Achieving the required calculation speed necessitates significant computing resources, which can be organized in data centers (DC).
Modern DCs, forming the core of any IS, can provide exceptionally high levels of availability, reliability, and data security in operational production planning. Typically, DCs are equipped with security mechanisms such as gateway filtering, communication channel protection (VPN/SSL VPN), intrusion prevention (IDS/IPS), client network segmentation, and access control to resources.
Consolidating computing resources in DCs allows enterprises to reduce overall IT costs by lowering administration expenses and making more efficient use of technical means. Modern large corporations and holdings are increasingly opting for a network-centric model of corporate information system construction, where all the company's data, services, and applications are stored and executed centrally in one DC. These factors have increased client interest in DC-based services in the global market. A global trend is the transition to infrastructure services IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
There is a shortage of MES-class information systems on the global market designed for operational production management with the capability to provide services via the SaaS model. One such solution is C-MES: SaaS, which provides an API interface for performing complex computations in the cloud and obtaining ready-made production schedules.
C-MES: SaaS was initially developed as a SaaS solution, incorporating the latest cloud computing technologies. In particular, modern encryption technologies are used, ensuring secure commercial information exchange over the network. The primary task of C-MES: SaaS is to process data characterizing the production process, generate and deliver information to the user in a standardized form. C-MES: SaaS provides information on client orders, production technology, equipment parameters and availability, tooling, labor resources, as well as raw materials and supply schedules, and maps of optimal technological transitions. This data is utilized by systems such as "C-MES: Production Management" in the cloud variant for operationally managing production processes from the release of the production order to the finished product.
C-MES: SaaS can interact with "C-MES: Production Management" software modules, which integrate into Odoo ERP and 1C: ERP WE. These modules provide the user interface and allow the use of functions for calculating cutting maps and production schedules.
Currently, the modules integrate with C-MES: SaaS via API, with all calculations executed on our servers. The integration module with C-MES: SaaS is included in the set of our "C-MES: Production Management" product, supported by a subscription service. Payment for the service is made monthly, and tariff plans depend on server load. For this, a preliminary analysis of the client's needs (number of planning operations, parallel calculation capabilities, etc.) is conducted, with prices varying from 10 to 1,000 GBP per month.
Our SaaS service can be integrated via API with any ERP system supporting such integration, without changing the subscription cost. However, we only implement and support "C-MES: Production Management" for Odoo ERP and 1C: ERP WE, with C-MES: SaaS guaranteeing a standard level of service for these solutions, ensuring your enterprise operates 24/7.
Thus, the technologies implemented in C-MES: SaaS ensure efficiency, security, availability, and flexibility in solving production planning and management tasks in a highly dynamic demand environment and the need to minimize costs, which is particularly important for small and medium-sized businesses.
Application of cloud Infrastructure for operational production management